Bibliometrics Research in India: A Scientometric Assessment of High-Cited Publications During 1994-2023
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/jcitation.3.3.29Keywords:
Bibliometrics Research, India, High-Cited Publications, Citation, CollaborationAbstract
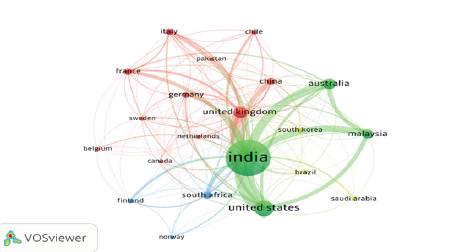
The present study examines the current status, key focus areas and emerging trends of published bibliometric research in India. The study retrieved and identified high-cited-papers related to India's bibliometrics research from the Scopus database using a predefined search strategy covering the years 1994-2023. For each downloaded record, the data elements included publication type, citation count, author count, institutional affiliations, country of origin and funding sources. Microsoft Excel was then used to analyze the data and examine collaborative connections among organizations, authors and keywords. The world and India has published 49, 049 and 3776 publications in bibliometrics research, of which 5341 and 309 have received 30 or more citations during 1994-23. Although, India ranks at 4th position in global output, but ranks at 9th position in terms of high-cited papers receiving 30 and more citations. The 309 HCPs from India were published in 193 different journals, with contributions from 1,101 authors, 471 of whom were Indian. The 309 Indian HCPs received a total of 24,670 citations, averaging 79.84 citations per paper. India's annual publication output varied over time, with consistent 10-year growth from 17 publications (1994-2003) to 47 (2004-2013) to 245 (2014-2023). External funding supported 20.39% of India's research output, while international collaboration accounted for 56.63% share. The most productive organizations were the Malaviya National Institute of Technology, Jaipur and the National Institute of Science, Technology and Development Studies, New Delhi. The most impactful organizations were the Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur and the Malaviya National Institute of Technology, Jaipur. The most prolific individual authors were S. Kumar and A. Pandey, with notable impact metrics. Scientometrics and the Journal of Business Research were the most productive, while the Journal of Business Research and the Journal of Clinical Orthopaedics and Trauma were the most impactful. These findings highlight India's significant contribution to high-cited publications, showcasing both productivity and impact in research output. This comprehensive bibliometric analysis provides an in-depth and enlightening overview of significant articles, journals, authors, institutions and themes in the field. Through this overview, by utilizing these valuable insights, researchers can swiftly grasp the present state, focal points and emerging patterns of bibliometric research in India during the throughout the last thirty years. To improve future studies, it is believed that To further enhance these discoveries, forthcoming studies the scientific community should strive to foster interdisciplinary and international cooperation among Indian scholars and organizations.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.



